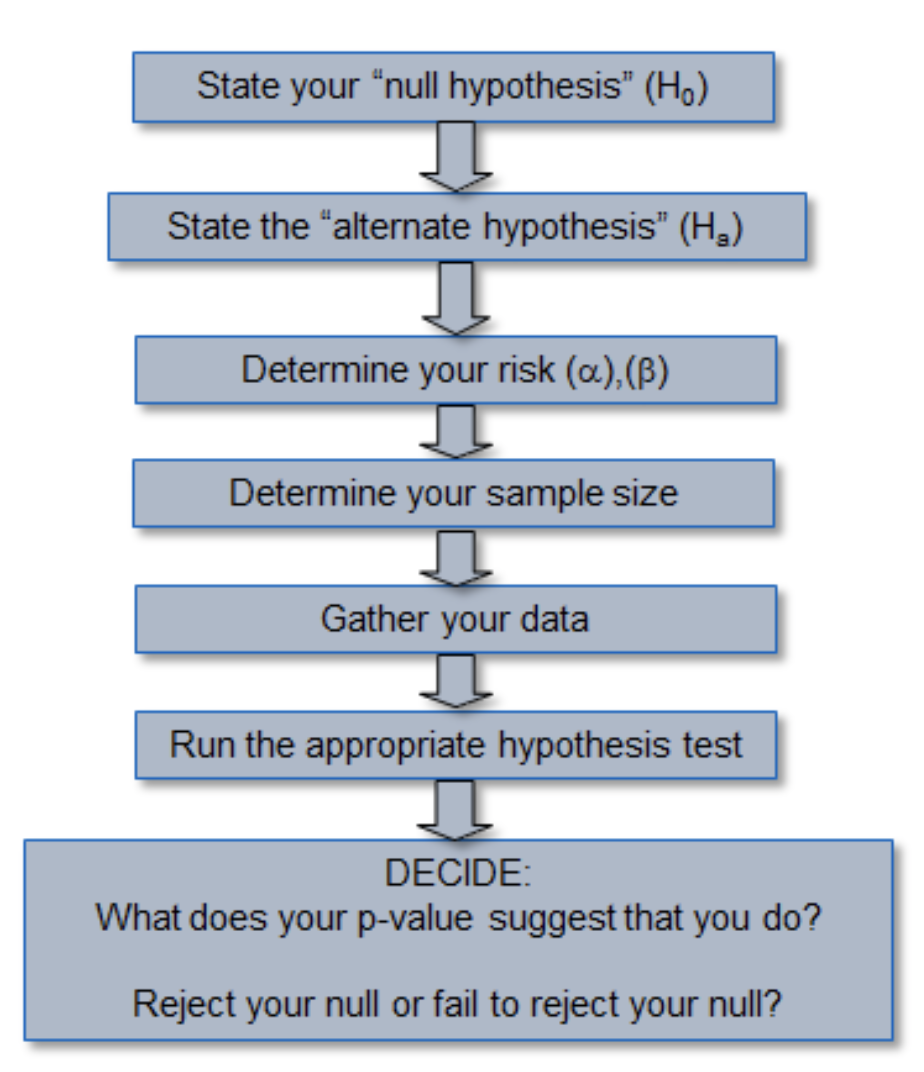
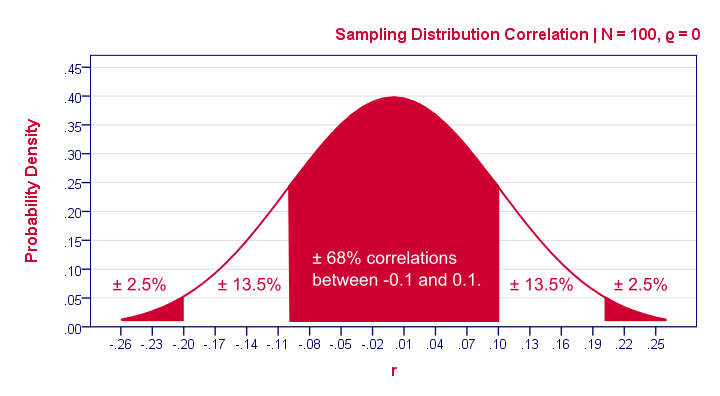
Andrew F Siegel, in Practical Business Statistics (Seventh Edition), 16 Hypothesis testing uses data to decide between two possibilities (called hypotheses) 1 It can tell you whether the results you are witnessing are just coincidence (and could reasonably be due to chance) or are likely to be real Some people think of hypothesis testing as a way of using statistics to make decisions Accepting or rejecting the null hypothesis based on pvalue and R value Based on the correlation of two measures in the following plot The pvalue tells there is a significant correlation between the two measures but the correlation coefficient R is close to zero that means there is no evidence of any relationship Therefore, we reject the null hypothesis, and accept the alternative hypothesis However, if the p value is below your threshold of significance (typically p < 005), you can reject the null hypothesis, but this does not mean that there is a 95% probability that the alternative hypothesis is true

Ap Statistics More About Tests And Intervals Ppt Download
It tells whether the hypothesis be accepted or rejected
It tells whether the hypothesis be accepted or rejected-By definition, an accepted hypothesis is what you are left with once H0 has been disproven, This is also called H1 Importantly, H1 has not not been but emerges from the ruins of the disproven H0 A rejected hypothesis should always be the state of not having been able to disprove H0 Any other use of the term will easily get you into troubleHow do you decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothell tentence 2 How do you tell whether the test bleft, right, or two talled bullets 3 Why can we never accept the null hypothesis



Chapter 3 Hypothesis Testing Natural Resources Biometrics
The result of the test will determine whether we accept or reject, but the pvalue gives usStatistic's under the null hypothesis •Measure of how likely the test statistic value is under the null hypothesis Pvalue ≤ α ⇒ Reject H 0 at level α Pvalue > α ⇒ Do not reject H 0 at level α •Calculate a test statistic in the sample data that is relevant to the hypothesis being tested Variance of a sample tells a statistician about dispersion of the random variable from its mean It is the second moment whether the hypothesis analysis is accepted or rejected
To determine whether to reject the null hypothesis using the tvalue, compare the tvalue to the critical value The critical value is t α/2, n–p1, where α is the significance level, n is the number of observations in your sample, and p is the number of predictors If the absolute value of the tvalue is greater than the critical value, you reject the null hypothesisBased on the outcome of the hypothesis test one hypothesis is rejected and accept the other based on a previously predetermined arbitrary benchmark This bench mark is designated the P value However, one runs into making an error one may reject one hypothesis when in fact it should be accepted and vise versaWhereas the alternative hypothesis relates to the statement to be accepted if / when the null is rejected The final conclusion, once the test has been carried out, is always given in terms of
This leads us to reject H0 and accept the alternative hypothesis This probability is nothing but the pvalue in hypothesis testing When the probability of observation by considering H0 is true falls below the threshold value/alpha/level of significance (ie 005) we reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis The pvalue doesn't determine whether we accept or reject the null hypothesis; Decision Rule Calculator In hypothesis testing, we want to know whether we should reject or fail to reject some statistical hypothesis To make this decision, we compare the pvalue of the test statistic to a significance level we have chosen to use for the test If the pvalue is less than the significance level, we reject the null hypothesis




Solved 63 In A Test Of Hypotheses The Hypothesis We Start Chegg Com



Hypothesis Testing Definition
The pvalue (or the observed level of significance) is the smallest level of significance at which you can reject the null hypothesis, assuming the null hypothesis is true You can also think about the pvalue as the total area of the region of rejection Remember that in a onetailed test, the regi In statistics, we use hypothesis tests to determine whether some claim about a population parameter is true or not Whenever we perform a hypothesis test, we always write a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis, which take the following forms H 0 (Null Hypothesis) Population parameter = ≤, ≥ some value H A (Alternative Hypothesis) PopulationThe P value is the universal measure that is used in hypothesis testing to determine whether to reject the Null hypothesis or fail to reject it Each hypothesis test will calculate the appropriate P value based upon the test statistic When to use P Values are associated with all hypothesis tests




Hypothesis Testing An Example Hypothesis Testing Situation Sid Says That He Has Psychic Powers And Can Read People S Thoughts To Test This Claim A Ppt Download




Ap Statistics More About Tests And Intervals Ppt Download
If it is greater than α, you fail to reject H 0 Your decision can also be based on the confidence interval (or bound) calculated using the same αIn general a p value of 005 or greater is considered critical, anything less means the deviations are significant and the hypothesis being tested must be rejected of less than 050, but greater than 025 (Follow blue dotted line and arrows in Fig 5)Set the significance level, α, the probability of making a Type I error to be small — 001, 005, or 010 Compare the P value to α If the P value is less than (or equal to) α, reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis If the P value is




Examples Identifying Type I And Type Ii Errors Video Khan Academy




Using Spss For T Tests
If the null hypothesis is rejected, then we accept the alternative hypothesis If the null hypothesis is not rejected, then we do not accept the alternative hypothesis Going back to the above example of mean human body temperature, the alternative hypothesis is "The average adult human body temperature is not 986 degrees Fahrenheit"In the same way, a statistical test cannot prove the null hypothesis, but it can provide evidence against it As for the alternative hypothesis, it may be appropriate to say "the alternative hypothesis was not supported" but you should avoid saying "the alternative hypothesis was rejected" Once again, this is because your study is designed to reject the null hypothesis, not to reject the alternative hypothesisRejecting the Null We now have all the pieces of information to either accept the Null Hypothesis or to reject it In the table above, we want the twotailed test, and a significance level of p=005 Our df as we know = 30 Run down the column for 005 till you reach the row for df=30 The value in the table is 42
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/HypothesisTestinginFinance4-deefaac530e74d2880cf92a461b4c1fb.png)



Hypothesis Testing In Finance Concept And Examples




6 Hypothesis Testing Marketing Research Design Analysis 21
In Hypothesis testing, if the significance value of the test is greater than the predetermined significance level, then we accept the null hypothesis If the significance value is less than the predetermined value, then we should reject the null hypothesis A statistical test is a way to determine whether the random variable is following the null hypothesis or alternate hypothesis It basically tells whether the sample and population or two/ more samples have significant differences You can use various descriptive stats such as mean, median, mode, range, or standard deviation for this purpose1 Ans To decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis we consider the following two conditions such as;



Data Analysis In The Geosciences



Introduction To Hypothesis Testing In R Learn Every Concept From Scratch Dataflair
Clearly in that case we wouldn't want to accept the null hypothesis as it isn't true Ideally we should perform a power analysis to find out if we can reasonably expect to be able to reject the null hypothesis when it is false, however this isn't usually nearly as straightforward as performing the test itself, which is why it is usually neglectedRemember that the decision to reject the null hypothesis (H 0) or fail to reject it can be based on the pvalue and your chosen significance level (also called α) If the pvalue is less than or equal to α, you reject H 0;The critical value for conducting the lefttailed test H0 μ = 3 versus HA μ < 3 is the t value, denoted t( α, n 1) , such that the probability to the left of it is α It can be shown using either statistical software or a t table that the critical value t005,14 is That is, we would reject the null hypothesis H0 μ = 3



Data Analysis In The Geosciences



Null Hypothesis Quick Introduction
The first thing to recognize is that failing to reject the null hypothesis might not be an error If the null hypothesis is false, then the correct outcome is failing to reject the null However, if the null hypothesis is false and you fail to reject, it is a type II error, or a false negativeIn this case, the null hypothesis is rejected and an alternative hypothesis is accepted in its place If the data is consistent with the null hypothesis statistically possibly true, then the null hypothesis is not rejected In neither case is the null hypothesis or its alternative proven;Conclusions are sentence answers which include whether there is enough evidence or not (based on the decision), the level of significance, and whether the original claim is supported or rejected Conclusions are based on the original claim, which may be the null or alternative hypotheses The decisions are always based on the null hypothesis
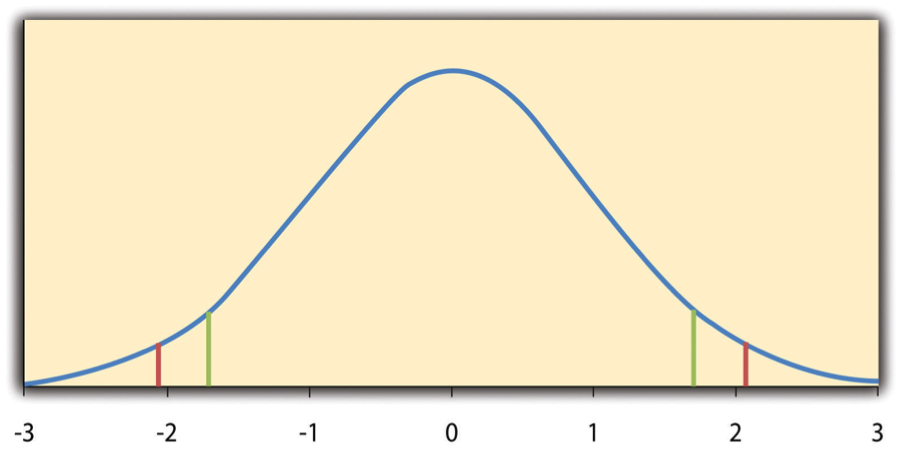



Some Basic Null Hypothesis Tests Research Methods In Psychology 2nd Canadian Edition
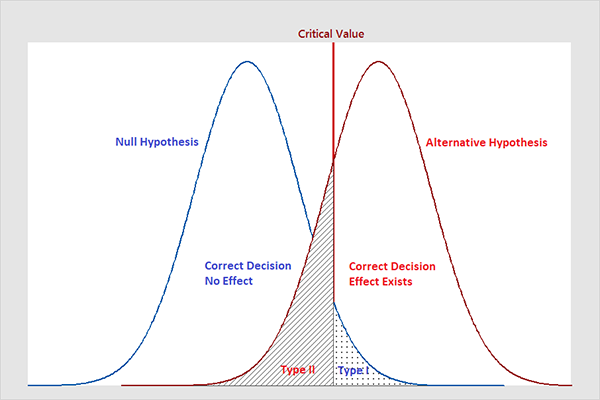



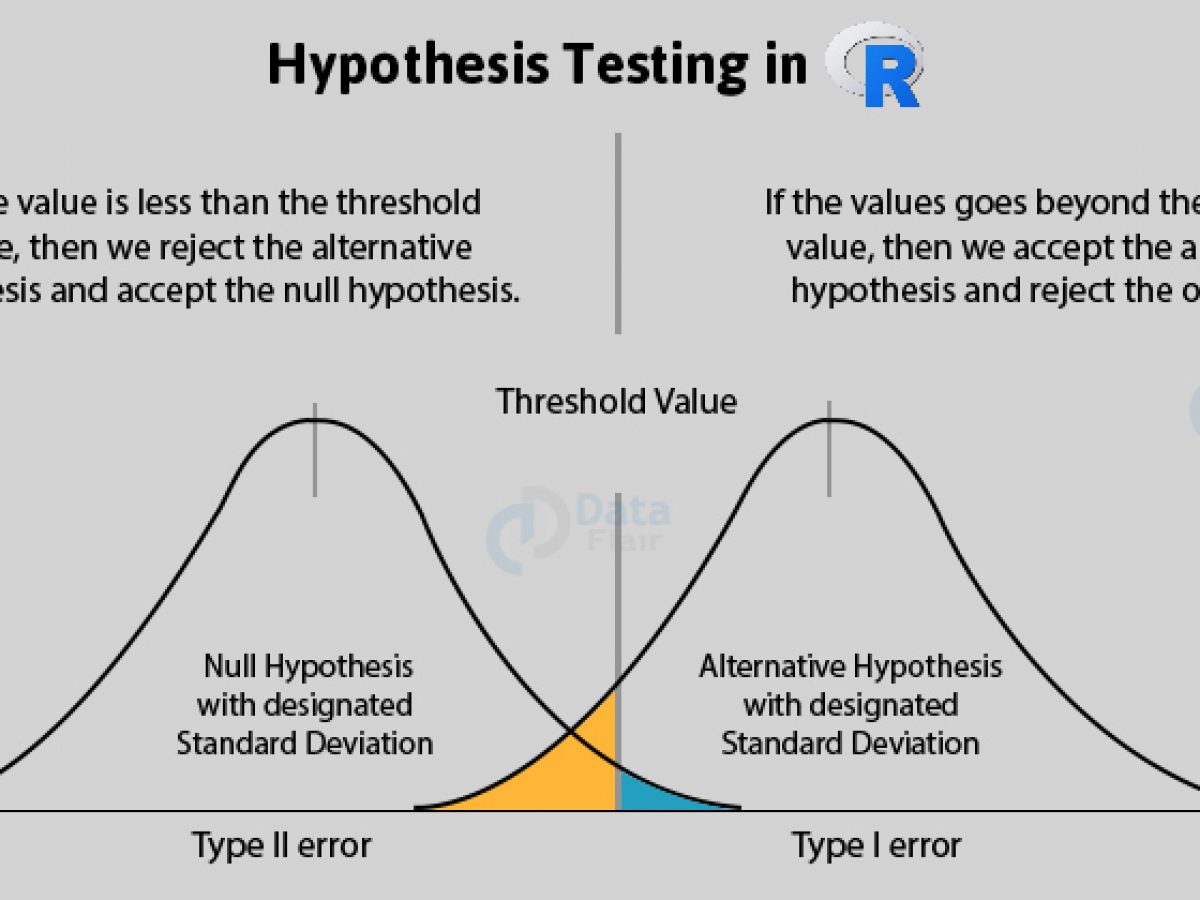
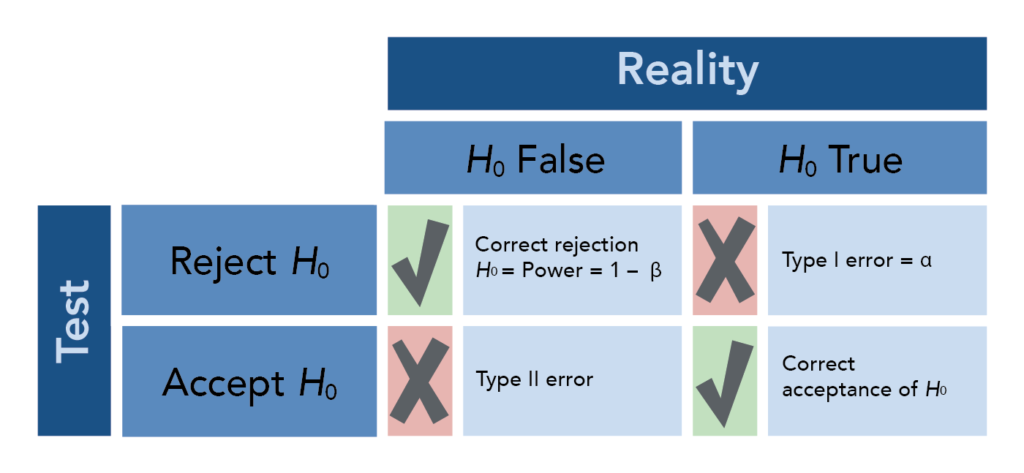
Types Of Errors In Hypothesis Testing Statistics By Jim
With better or more data, the null may still be rejected What does the F statistic tell you?A) accept the null hypothesis when it is true b) fail to reject the alternative hypothesis when it is false c) fail to reject the null hypothesis when it is false d) report that our findings are significant when they are not
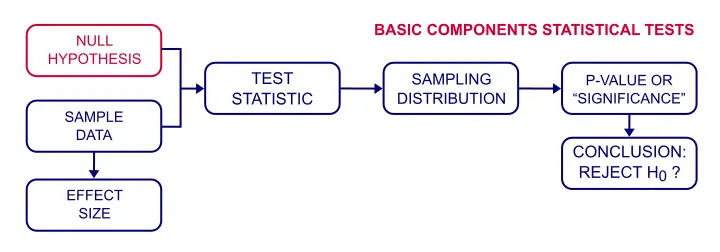



Null Hypothesis Quick Introduction




Chapter 10 Summary Stat213 Chapter 10 Hypothesis Testing Using A Single Sample 10 1 Hypotheses Studocu
Whether or not to accept the hypothesis depends on other factors, including the consequences of being wrong and established norms For example, in science, a "pvalue" of less than 005 is the generally accepted standard for accepting the hypothesis It means that the hypothesis Here We have some Boolean results basically these Boolean values tell whether we should accept or reject the null hypothesisAs from the above table there is significant mean difference betweenThe pvalue is a descriptor of the test itself The pvalue tells us "how good" the test is (in a certain sense of "how good"), even before the we perform the test;




Hypothesis Testing Tool



1
The first type of error is if the jury finds someone guilty refuses to accept H0, even though the person is innocent H0 is true The second type of error would be when the jury releases the person does not reject H0 although the person is guilty H1 is trueWe tend to want to reject the null hypothesis so we assume it is true and look for enough evidence to conclude it is incorrect We tend to want to accept the alternative hypothesis If the null hypothesis is rejected then we must accept that the alternative hypothesis is true Note H 0 will ALWAYS have an equal sign (and possibly a lessBut it remains true in that the acceptance of a null hypothesis is a weak decision whereas rejection is strong evidence of the sample against the null hypothesis When the null hypothesis is rejected it means the sample has done some statistical work, but when the null hypothesis is accepted it means the sample is almost silent




P Value And Statistical Significance Simply Psychology




Null Hypothesis And Alternative Hypothesis With 9 Differences
Level of Significance A predetermined level of significance allows for the null hypothesis to either be rejected or accepted 11 The significance level that is widely used in academic research is 005, which is often reported as 'p = 005' or 'α = 005'The null hypothesis is rejected in favour of the alternative hypothesis if the calculated pvalue is less than the predeterminedThe Fstatistic is the test statistic for Ftests In general, an Fstatistic is a ratio of two quantities that are expected to be roughly equal under the null hypothesis, which produces an Fstatistic of approximately 1 In order to reject the null hypothesis that the group means are equal, we need a high FThe pvalue is the chance you are wrong if you decide to reject the null hypothesis based on the data observed Can you tolerate this chance of error when rejecting the null hypothesis?



Data Analysis In The Geosciences




Solved Question 3 10 Points 3 To Your Surprise You Tind An Isolated Population Of Harlequin Ladybugs On An Island You Recall From Your Evolution Class That Small Species Tend To Become Larger
These tests allow the researcher to decide whether to accept or reject the null hypothesis and whether to accept or reject the alternative hypothesis If changes in the DV are due to chance then we'll accept the null hypothesis, whereas if the statistical test shows the change in the DV occurred due to the IV, then we accept the alternative hypothesis Important thing #1 A nonsignificant result does not allow you to accept the null hypothesis This is a ridiculously common mistake Suppose you're comparing the heights of a group of men against the heights of a group of women using a ttest The ttest spits out a pvalue of 03, which is higher than your chosen significance level 005 Failing to Reject vs Accept In an experiment, the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis should be carefully formulated such that one and only one of these statements is true If the collected data supports the alternative hypothesis, then the null hypothesis can be rejected as false




Hypothesis Testing For Means Proportions




Solved 1 Define A Problem Where You Test A Hypothesis Mean Chegg Com
When your pvalue is less than or equal to your significance level, you reject the null hypothesis The data favors the altern View the full answerIf this level of risk of error can be tolerated then the null hypothesis can be rejected




Hypothesis Testing Pdf Statistical Hypothesis Testing Type I And Type Ii Errors




Hypothesis Testing Maths Libguides At La Trobe University
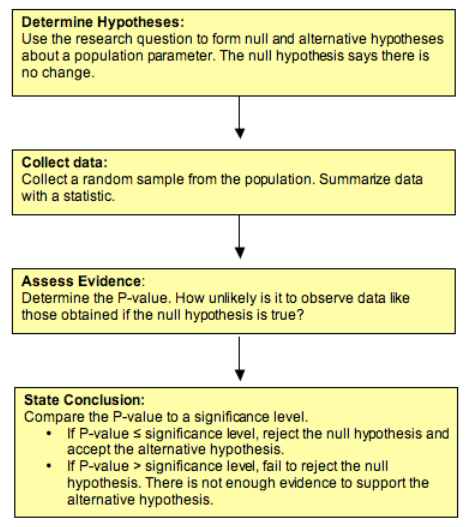



Hypothesis Testing 3 Of 5 Concepts In Statistics
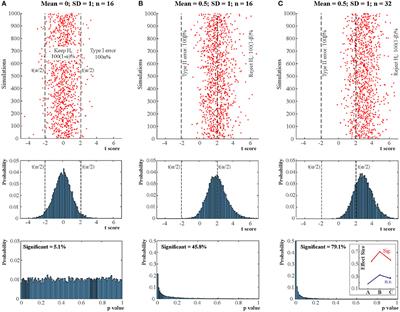



Frontiers When Null Hypothesis Significance Testing Is Unsuitable For Research A Reassessment Human Neuroscience




Failing To Reject The Null Hypothesis Statistics By Jim



Hypothesis Testing Using T Test Using Inferential Statistics Python By Pramodaiml The Startup Medium




Chapter 3 Hypothesis Testing Natural Resources Biometrics




Hypothesis Wikipedia
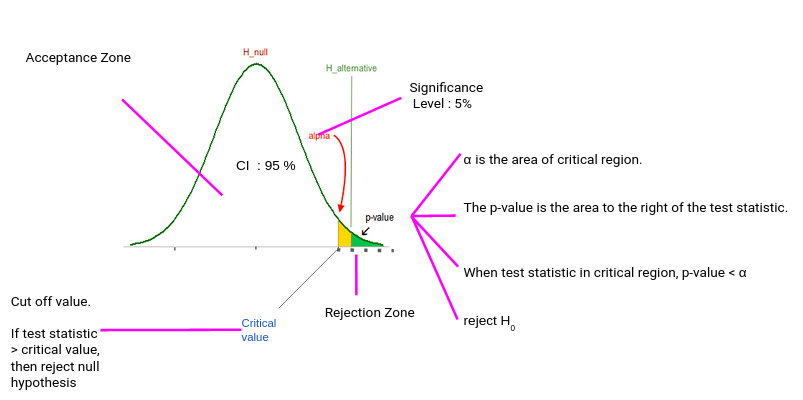



Hypothesis Testing Difference Between Z Test And T Test



Ocf Berkeley Edu




Comparing P Values To Different Significance Levels Video Khan Academy
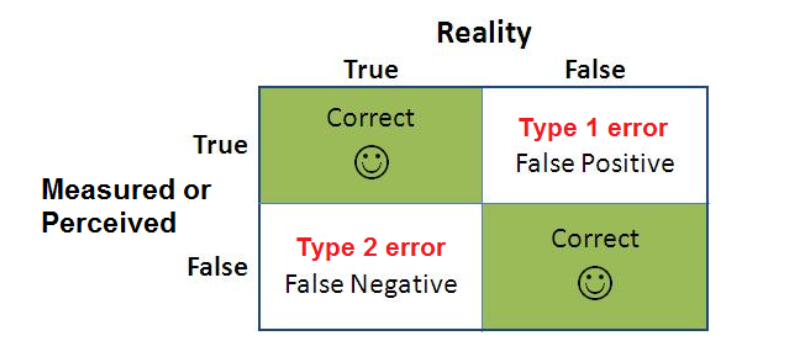



Everything You Need To Know About Hypothesis Testing Part I By Mahesh Towards Data Science




Hypothesis Testing Critical Values Rejection Regions I Statistics 101 4 Marinstatslectures Youtube




Hypothesis Testing P Value A Simplified Approach By Suraj Gurav Towards Data Science



1
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/HypothesisTestinginFinance1_2-1030333b070c450c964e82c33c937878.png)



Hypothesis Testing In Finance Concept And Examples




What Are Type I And Type Ii Errors Simply Psychology




Hypothesis Testing Maths Libguides At La Trobe University




Hypothesis Testing Definition Examples




Solved Which Of Tue Following In The Rejection Area Statements When The Null Would Be Applicable The Ifthe Calculated Value Of Tcsl Statistic Falls Decision Is Hypothesis Ho Is Alse A Type Correct
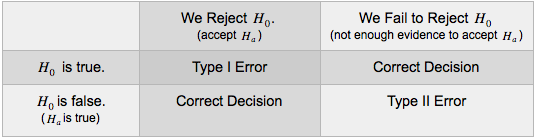



Hypothesis Testing 5 Of 5 Concepts In Statistics
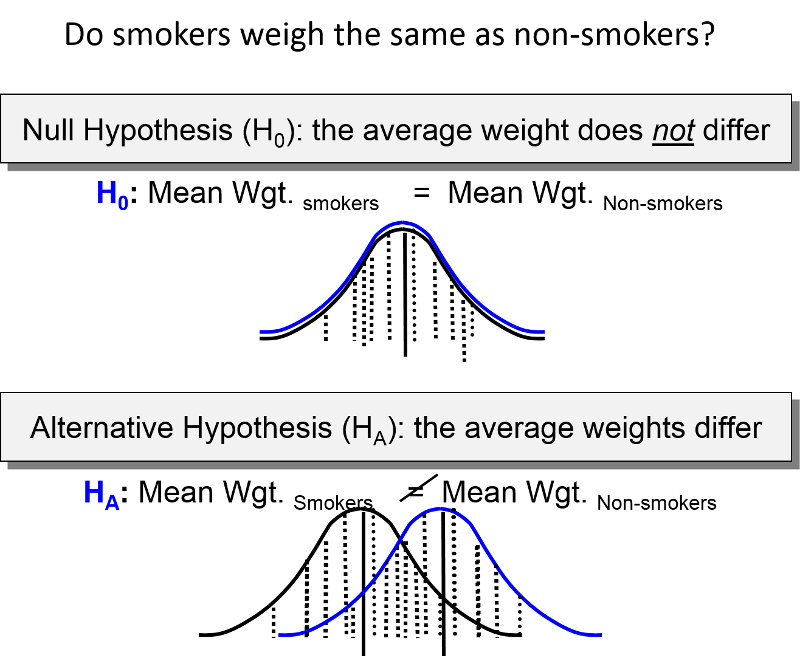



Hypothesis Testing



Hypothesis Testing 5 Of 5 Concepts In Statistics
/null-hypothesis-vs-alternative-hypothesis-3126413-v31-5b69a6a246e0fb0025549966.png)



Null Hypothesis And Alternative Hypothesis
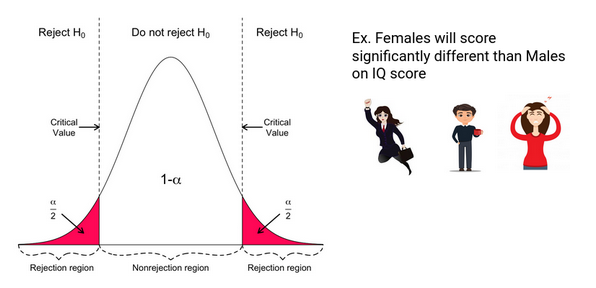



Hypothesis Testing Difference Between Z Test And T Test



1
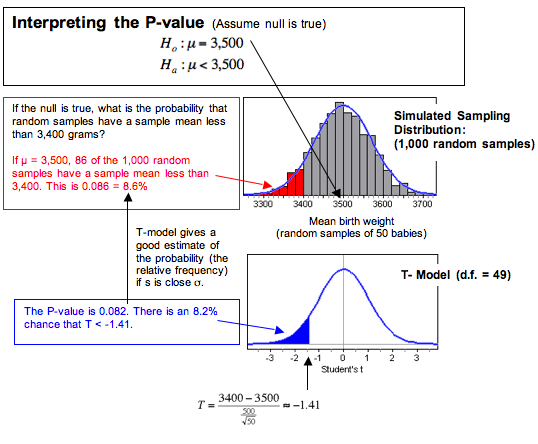



Hypothesis Test For A Population Mean 5 Of 5 Concepts In Statistics




Solved Problem 1 6 Points Total For Cach Of The Following Scenarios Please List The Critical Value S You Would Use To Determine Whether You Would Acecpt Or Reject Your Null Hypothesis If You



1
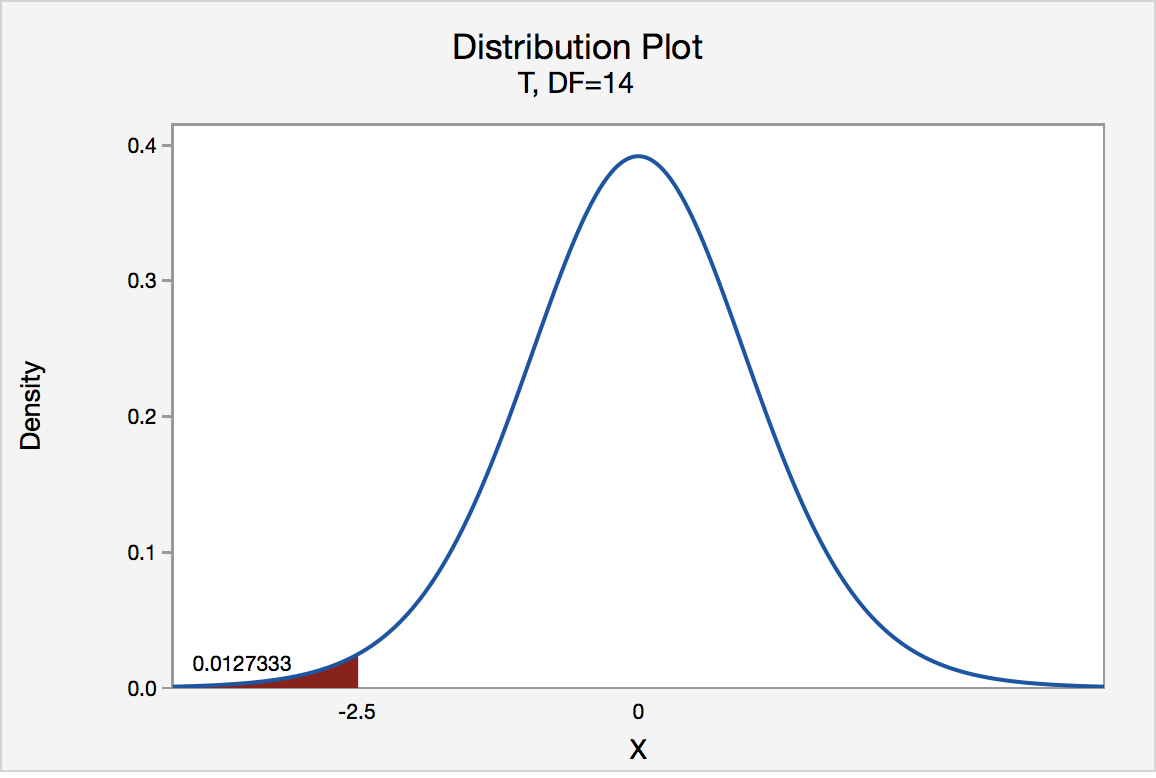



S 3 2 Hypothesis Testing P Value Approach Stat Online




Master Hypothesis Testing In Statistics Guide



Hypothesis Testing Statistically Significant P Value



2
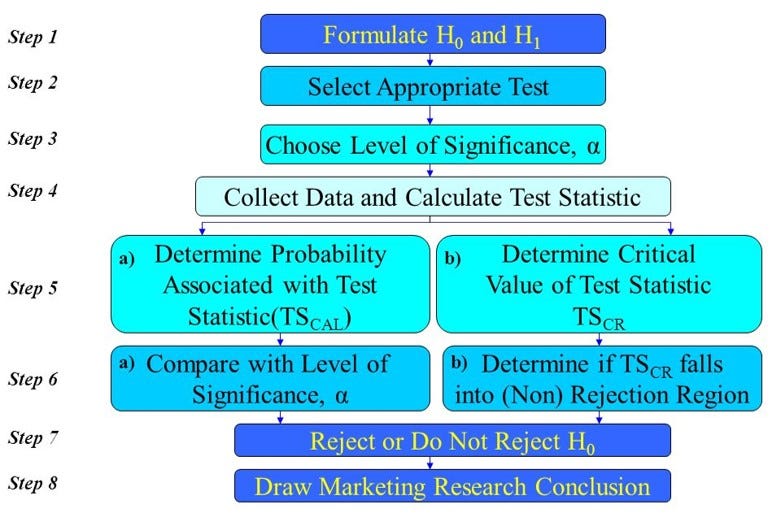



Everything You Need To Know About Hypothesis Testing Part I By Mahesh Towards Data Science
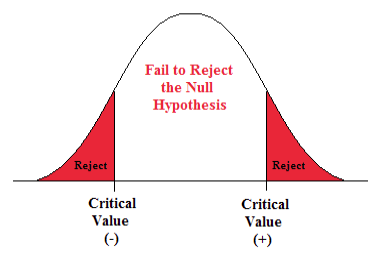



Chapter 3 Hypothesis Testing Natural Resources Biometrics




P Value And Statistical Significance Simply Psychology



Step 5 Interpreting The Results Chi Square Test For Goodness Of Fit In A Plant Breeding Example Passel




Hypothesis Testing All A Beginner Needs To Know By Abhishek Barai Analytics Vidhya Medium



Hypothesis Testing Calculator



2
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/HypothesisTestinginFinance2_2-8b3d4def38c945e8940385f1382b7ec4.png)



Hypothesis Testing In Finance Concept And Examples
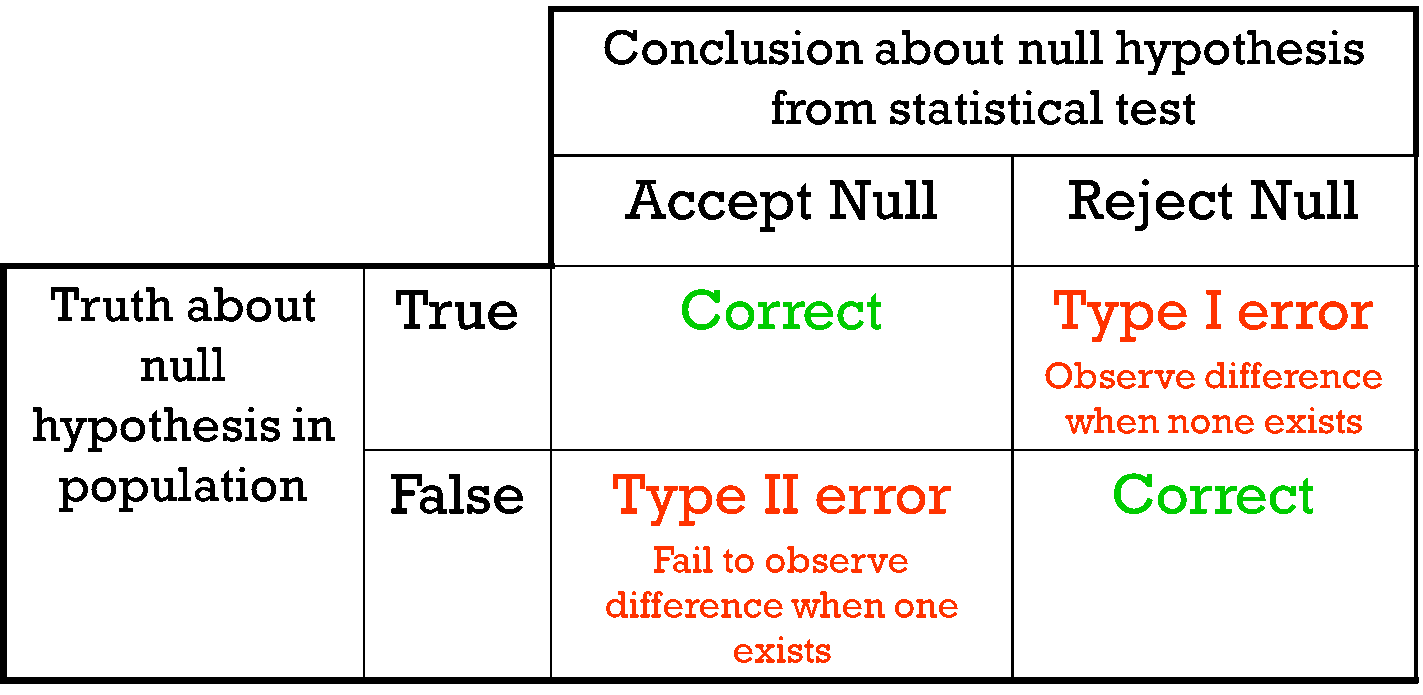



Hypothesis Testing Maths Libguides At La Trobe University




Inferential Statistics Ppt Download




Developing And Testing Hypotheses Skillsyouneed




Statistics Rd Wi Fo R E T A
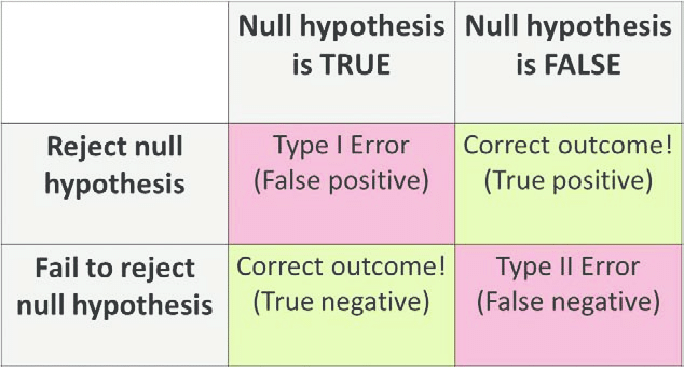



Hypothesis Testing Statistically Significant P Value




Null Hypothesis Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary
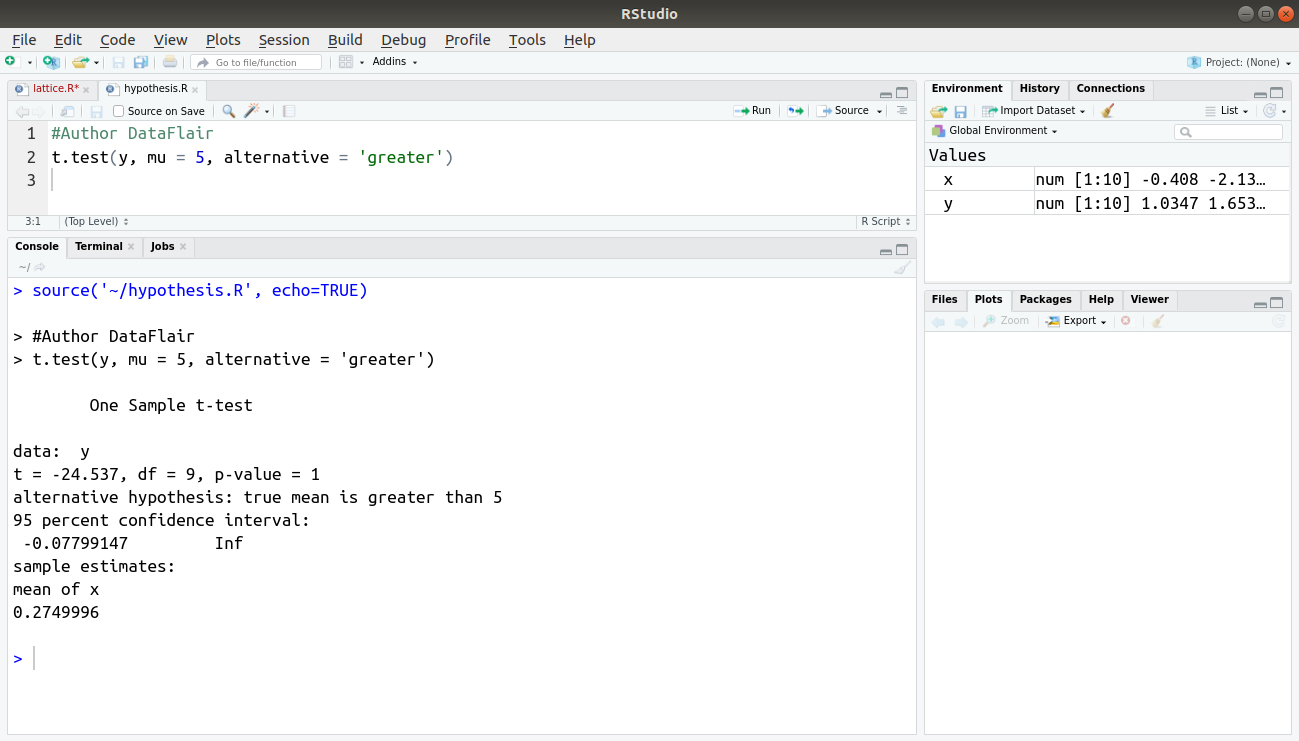



Introduction To Hypothesis Testing In R Learn Every Concept From Scratch Dataflair



2
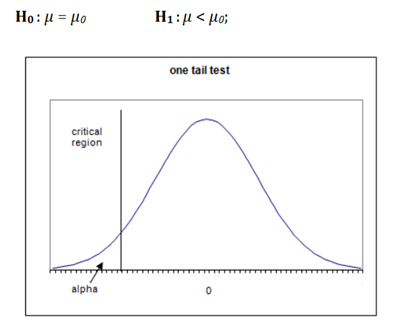



Hypothesis Testing Statistically Significant P Value




Hypothesis Testing Maths Libguides At La Trobe University




One Tailed And Two Tailed Hypothesis Tests Explained Statistics By Jim




Hypothesis Testing And P Values Video Khan Academy
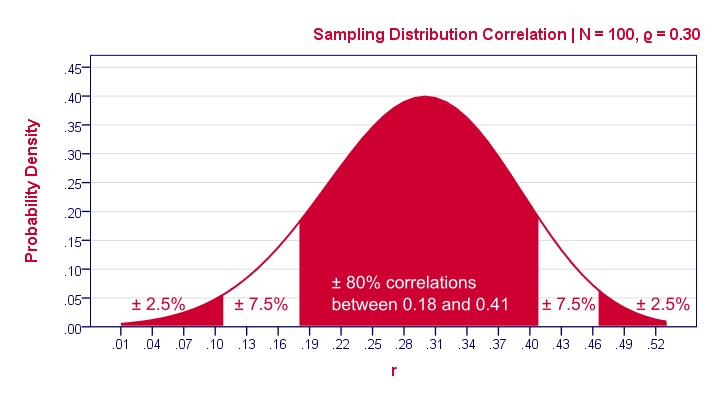



Null Hypothesis Quick Introduction
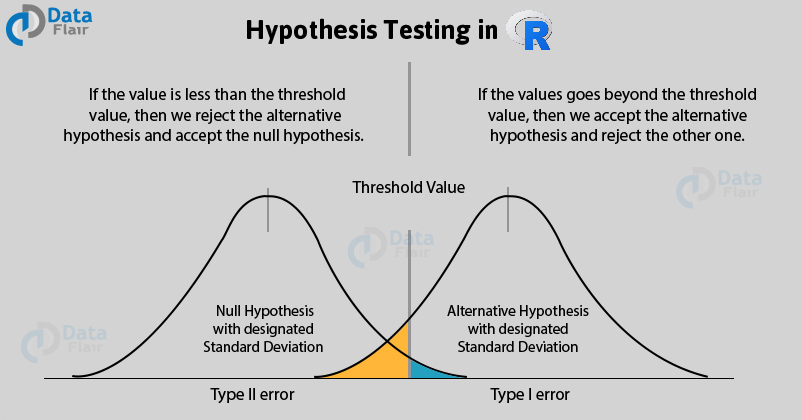



Introduction To Hypothesis Testing In R Learn Every Concept From Scratch Dataflair
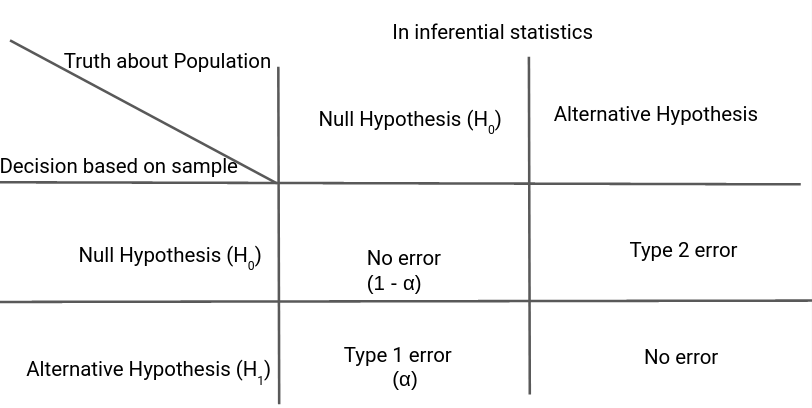



Hypothesis Testing Difference Between Z Test And T Test




Frontiers When Null Hypothesis Significance Testing Is Unsuitable For Research A Reassessment Human Neuroscience



2




Anova And Pca Pdf Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors Principal Component Analysis




Hypothesis Testing How To Find Rejection Regions And Critical Values Using A Z Test Youtube




Hypothesis Testing Dr Richard Jackson Ppt Download
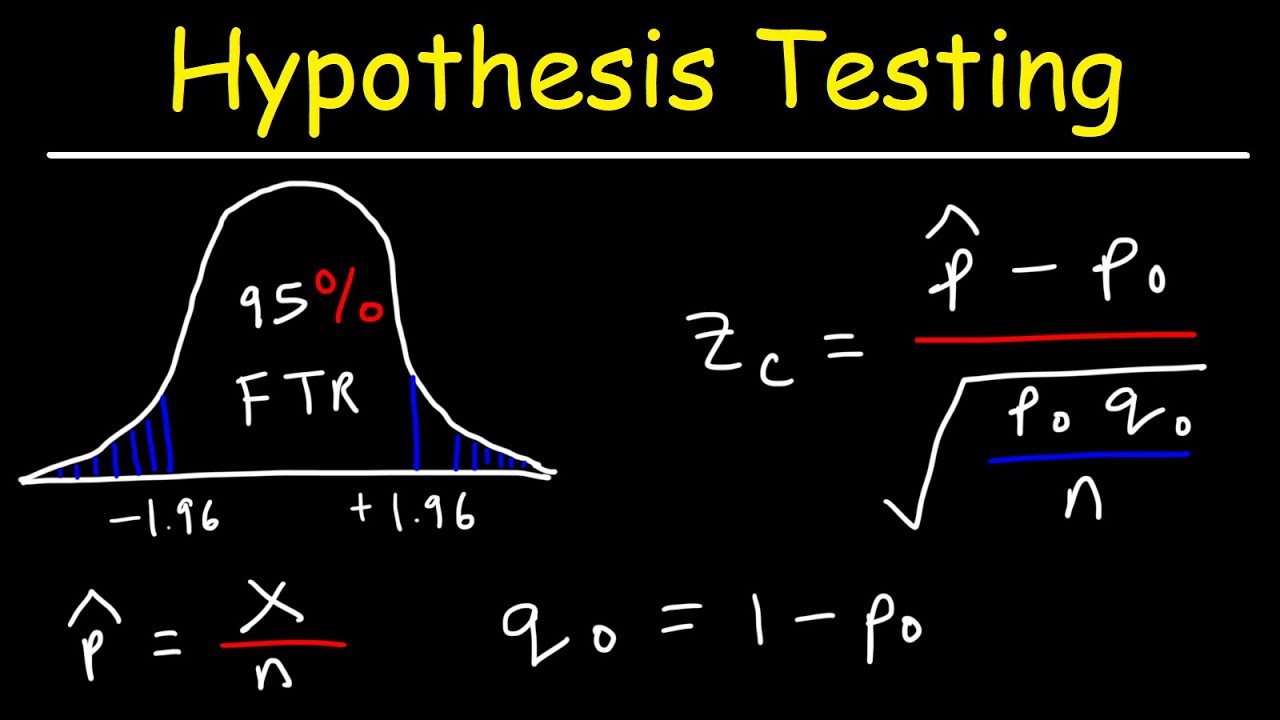



Hypothesis Testing Problems Z Test T Statistics One Two Tailed Tests 2 Youtube
/null-hypothesis-vs-alternative-hypothesis-3126413-v31-5b69a6a246e0fb0025549966.png)



Null Hypothesis And Alternative Hypothesis
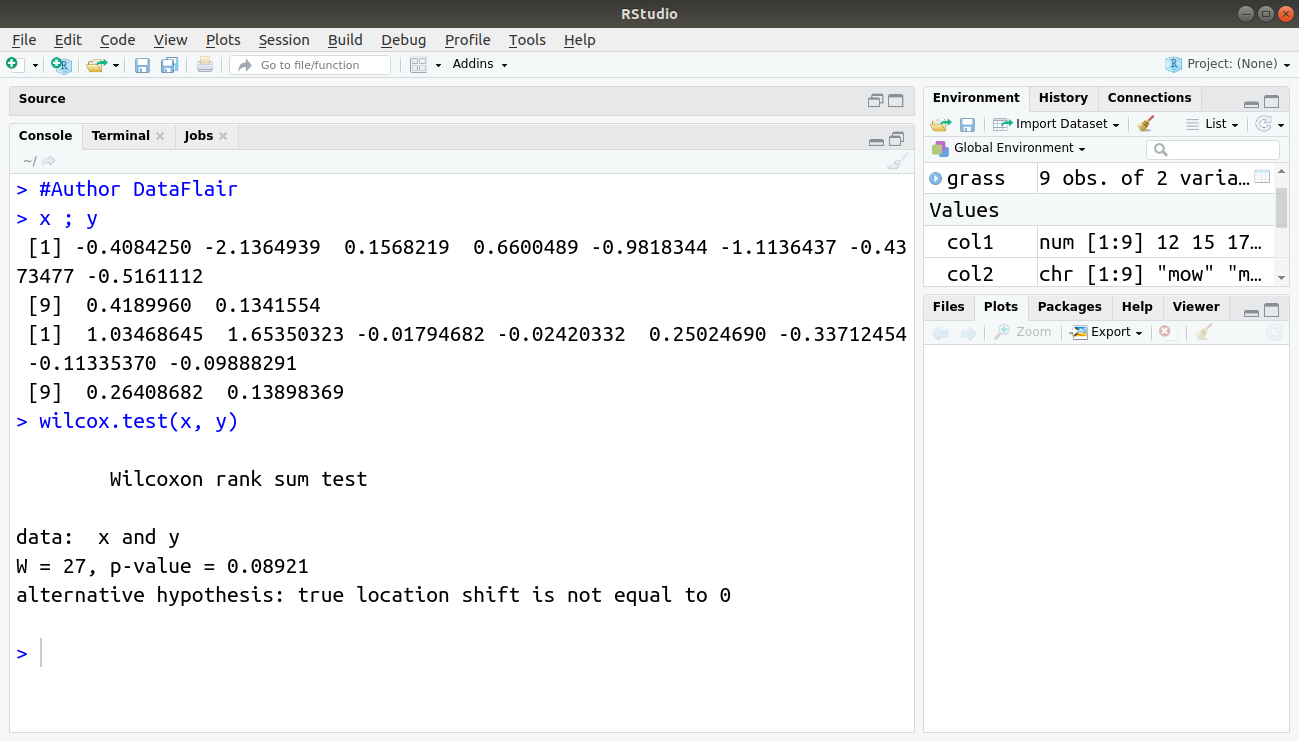



Introduction To Hypothesis Testing In R Learn Every Concept From Scratch Dataflair




Constructing Hypotheses For A Significance Test About A Proportion Video Khan Academy




Scientific Hypothesis Definition Formulation Example Britannica




Everything You Need To Know About Hypothesis Testing Part I By Mahesh Towards Data Science



Hypothesis Testing Handbook Of Biological Statistics




In Hypothesis Testing A Test Statistic Is O The Chegg Com
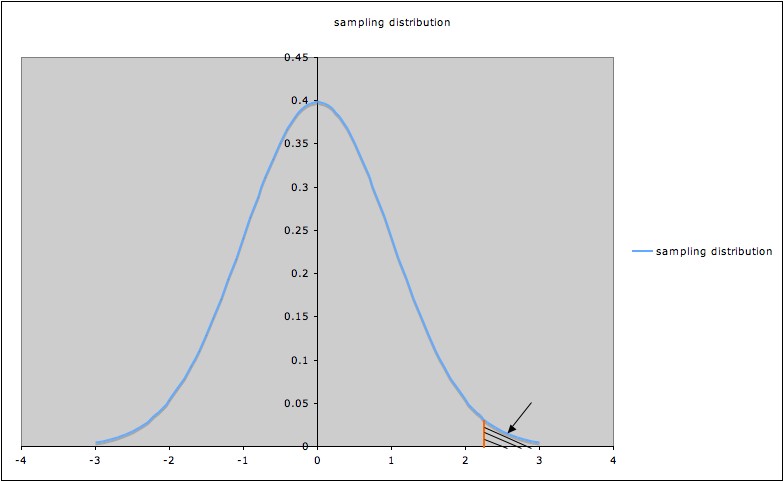



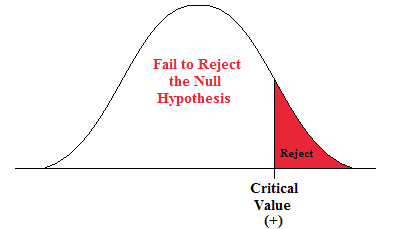
Rejection Region Critical Region For Statistical Tests Statistics How To
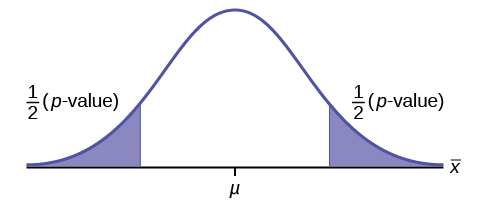



Full Hypothesis Test Examples Introductory Business Statistics
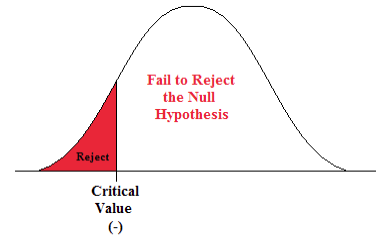



Chapter 3 Hypothesis Testing Natural Resources Biometrics



2
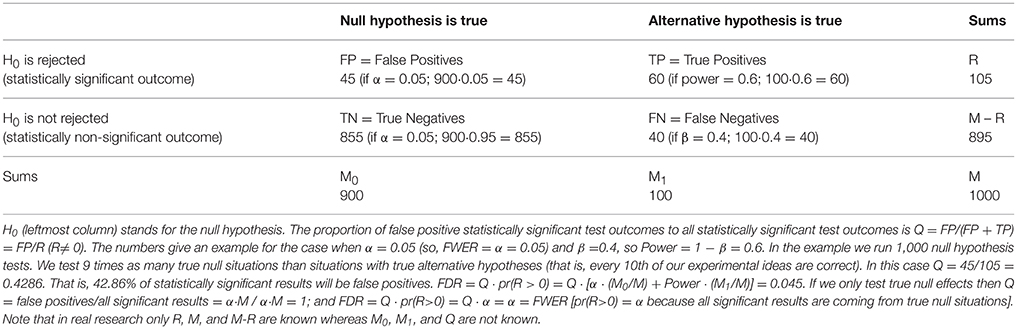



Frontiers When Null Hypothesis Significance Testing Is Unsuitable For Research A Reassessment Human Neuroscience




B Decide Whether The Null Hypothesis Is To Be Rejected Or Accepted Given The Test Value And The Brainly Ph
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Two_Tailed_Test_Sep_2020-01-b86f83d6c5f64f1a8e091d1cb0cd5f67.jpg)



Two Tailed Test Definition




Failing To Reject The Null Hypothesis Statistics By Jim




Failing To Reject The Null Hypothesis Statistics By Jim




Review Estimating A Mean Suppose We Want To




A Null Hypothesis Can Only A Be Accepted B Chegg Com



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿